Types of Motor Oil ..
Motor oil can be segmented into four basic varieties—Synthetic oil, Synthetic blends, High mileage oil and Conventional oil.
Synthetic motor oil is a laboratory synthesis of precisely controlled ingredients created by oil engineers, scientists and chemists. When combined with a high-performance additive package, this results in an oil with the highest levels of lubrication and engine protection, generally offering better protection at startup, better cleansing qualities, enhanced durability and better protection against heat buildup.
Synthetic blend motor oils use a mixture of synthetic and conventional base oils for added resistance to oxidation (compared to conventional oil) and to provide excellent low-temperature properties and are recommended for cars, trucks, vans and SUVs that regularly carry heavy loads, tow trailers and/or operate frequently at high RPMs.
High-mileage motor oil is specially blended for older vehicles, or vehicles with higher mileage. Typically, 75,000 miles (120,000 kilometers) is the figure used regarding high mileage oil. Some high mileage, high-performance cars, however, will be better served by continuing to use a synthetic motor oil. That said, a special high mileage motor oil blend, with its unique additives and viscosity, helps reduce oil burn-off, helps in sealing oil leaks and helps improve combustion chamber sealing to help restore engine compression. It all adds up to enhanced performance in older engines.
Conventional motor oil is what its name implies—it uses base oils enhanced in the blending process with chemical additives to help meet the manufacturer's desired levels of heat tolerance, breakdown resistance and viscosity (viscosity simply being a technical term for the thickness and fluidity of the oil). Conventional motor oil can be had in a range of viscosity grades and quality levels, from adequate to an extensively designed, high-quality lubricant. Conventional motor oil is recommended for drivers with low-mileage, late-model cars whose driving habits can be described as routine—commuting, running errands, vacation driving at relaxed cruising speeds. Today more and more engines require synthetic oil, so be sure to check your owner’s manual to make sure you don’t invite avoidable engine problems or void your warranty.
OIL GRADE DESIGNATIONS
Motor oils use a rating system developed by SAE, which is the Society of Automotive Engineers, to classify oil by viscosity. We’re all used to seeing designations like SAE 5W-30 or SAE 10W-30, so let’s talk about what they really mean.
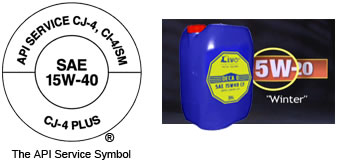
For multi-grade viscosity oils, the cold-temperature viscosity is labeled with a “W,” which stands for “winter.” Thus, in an SAE 10W-30 oil, the “10” is the cold-temperature viscosity rating, and the “30” is the high-temperature viscosity rating. This combination provides an oil that flows well at low temperatures, but still protects the engine at high temperatures.
For comparison’s sake, SAE 5W-30 and SAE 0W-30 will flow better at even lower temperatures than 10W-30 while still providing protection at high temperatures. Just remember, the “W” stands for winter.
Please refer to your owner’s manual or our Oil Selector tool to ensure you are using the recommended motor oil for your vehicle.
You see this symbol on many quality oils. API is an acronym for the American Petroleum Institute. The institute’s Starburst stamp of approval—it reads “American Petroleum Institute Certified”—was created to help consumers identify engine oils that meet specific performance standards set by vehicle and engine manufacturers.

The Starburst identifies engine oils recommended for a certain application, such as “For Gasoline Engines.” To carry this symbol on the container, the oil must meet the most current requirements of ILSAC, which is the International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee, a joint effort of U.S. and Japanese automobile manufacturers.
The Starburst is typically found on the front label on SAE 0W-20, SAE 0W-30, SAE 5W-20, SAE 5W-30 and SAE 10W-30 motor oils.
The API “donut”
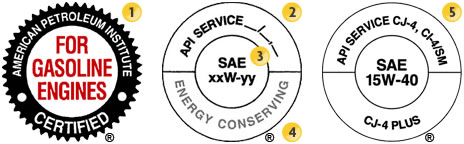
Another identifier on motor oil containers is the API “donut” typically found on the back label. It’s divided into three parts. The top half of the circle (2) indicates the API service rating, also called the performance level. The center of the circle (3) denotes the SAE viscosity, which we just discussed. The lower half of the circle (4) indicates whether the oil has demonstrated certain resource conserving or energy-conserving properties.
In the top part of the donut the words “API Service XXXXX” (5) indicate the type of engine and performance the oil provides. API Service SN the current rating means “S” for Service Station oil (for gasoline engines) and N the current level of service. Or it will say “API Service CJ-4.” API service CJ-4 means “C” for commercial engines (diesel engines) and J-4 where J is the current performance level and 4 indicates a 4-stroke diesel (a 2 will be used for 2-stroke diesel engines).









